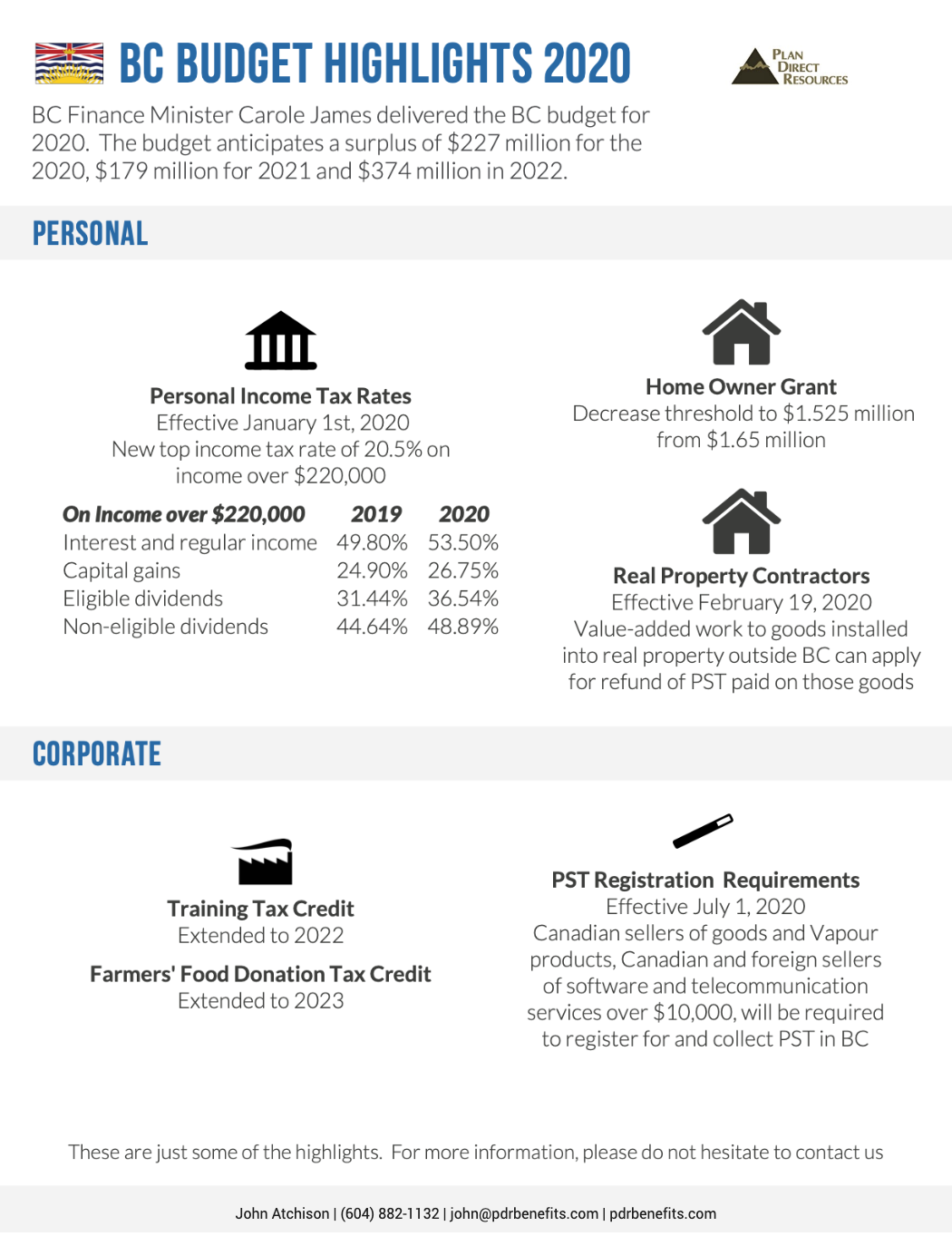
BC Government supporting renters, landlords during COVID-19
$500/month towards rent
To support people and prevent the spread of COVID-19, the Province is introducing a new temporary rental supplement, halting evictions and freezing rents, among other actions.
The new rental supplement will help households by offering up to $500 a month towards their rent, building on federal and provincial financial supports already announced for British Columbians facing financial hardship.
“Nobody should lose their home as a result of COVID-19. Our plan will give much-needed financial relief to renters and landlords. It will also provide more security for renters, who will be able to stay in their homes without fear of eviction or increasing rents during this emergency.” – Premier John Horgan
The funds will support renters experiencing a loss of income by helping them pay their rent and will be paid directly to landlords on their behalf, to ensure landlords continue to receive rental income during the pandemic. Benefiting people with low to moderate incomes, this supplement will be available to renters who are facing financial hardship as a result of the COVID-19 crisis, but do not qualify for existing rental assistance programs.
The Province is implementing a number of additional measures to keep people housed and protect their health. The full list of immediate measures includes:
-
The new temporary rent supplement will provide up to $500 per month, paid directly to landlords.
-
Halting evictions by ensuring a landlord may not issue a new notice to end tenancy for any reason. However, in exceptional cases where it may be needed to protect health and safety or to prevent undue damage to the property, landlords will be able to apply to the Residential Tenancy Branch for a hearing.
-
Halting the enforcement of existing eviction notices issued by the Residential Tenancy Branch, except in extreme cases where there are safety concerns. The smaller number of court ordered evictions are up to the courts, which operate independently of government.
-
Freezing new annual rent increases during the state of emergency.
-
Preventing landlords from accessing rental units without the consent of the tenant (for example, for showings or routine maintenance), except in exceptional cases where it is needed to protect health and safety or to prevent undue damage to the unit.
-
Restricting methods that renters and landlords can use to serve notices to reduce the potential transmission of COVID-19 (no personal service and allowing email).
-
Allowing landlords to restrict the use of common areas by tenants or guests to protect against the transmission of COVID-19.